Tutorials: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{| | == [[Evolutionary graph theory]] == | ||
| | {| | ||
| style="vertical-align:top" |[[Image:Superstar graph (N=484, B=21, k=6).svg|160px|left|link=Evolutionary graph theory]] | |||
[[ | | style="vertical-align:top" |Tutorial on [[evolutionary graph theory]], which provides a formal approach to describe the spreading and fixation (or extinction) of a mutant type in structured populations. Interestingly, the fixation probabilities remain unaffected by the underlying structure for a [[Moran graphs|large class of graphs]]. However, some graphs may act either as [[Evolutionary amplifiers|amplifiers]] or [[Evolutionary suppressors|suppressors]] of selection by increasing or decreasing the fixation probabilities as compared to unstructured populations. In contrast, fixation and absorption times are very sensitive to changes in the graph structure and hence vary greatly even for graphs that leave fixation probabilities unchanged. Even though fixation times are, in general, not preserved between graphs, [[Graph symmetries|symmetries of a graph]] can at least ensure that fixation times do not depend on the initial location of the mutant. This summarizes research efforts that span over a decade, including: | ||
| | <div class="footnote" style="font-size:smaller"> | ||
< | #Lieberman, E., Hauert, C. & Nowak, M. (2005) ''Nature'' '''433''' 312-316 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature03204 doi: 10.1038/nature03204]. | ||
#Jamieson-Lane, A. & Hauert, C. (2015) ''J. Theor. Biol.'' '''382''' 44-56 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.06.029 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.06.029]. | |||
#McAvoy, A. & Hauert, C. (2015) ''J. R. Soc. Interface'' '''12''' 20150420 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2015.0420 doi: 10.1098/rsif.2015.0420] | |||
</div> | |||
|} | |||
{{-}} | |||
== [[ | == [[Stochastic dynamics in finite populations]] == | ||
{| | |||
| style="vertical-align:top" |[[Image:RSP - SDE.svg|160px|left|link=Stochastic dynamics in finite populations]] | |||
| style="vertical-align:top" |Tutorial on the stochastic dynamics arising through demographic noise and mutations in finite populations of size \(N\). Comparisons of the deterministic replicator dynamics in the limit of infinite population sizes \(N\to\infty\) to the stochastic dynamics generated by stochastic differential equations, which are derived from a microscopic description of elementary changes in the population, as well as to results from individual based simulations. | |||
<div class="footnote" style="font-size:smaller"> | |||
#Traulsen, A., Claussen, J. C. & Hauert, C. (2012) ''Phys. Rev. E'' '''85''' 041901 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.85.041901 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.85.041901]. | |||
#Traulsen, A., Claussen, J. C. & Hauert, C. (2006) ''Phys. Rev. E'' '''74''' 011901 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.74.011901 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.74.011901]. | |||
#Traulsen, A., Claussen, J. C. & Hauert, C. (2005) ''Phys. Rev. Lett.'' '''95''' 238701 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.238701 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.238701]. | |||
</div> | |||
|} | |||
{{-}} | |||
Tutorial on | == [[Evolutionary Games and Population Dynamics]] == | ||
{| | |||
| style="vertical-align:top" | [[Image:Evolutionary games and population dynamics.gif|left|160x160px|link=Evolutionary Games and Population Dynamics]] | |||
| style="vertical-align:top" |Tutorial on frequency dependent selection in populations of varying size. The classic replicator dynamics assumes constant (infinite) population sizes and thus neglects the ecology of the population. Linking ecological dynamics and evolutionary games generates fascinating and rich dynamical behavior. Most importantly, however, this reveals a new mechanism for maintaining cooperation through negative feedback between population densities and the size of interaction groups. | |||
<div class="footnote"> Hauert, | <div class="footnote" style="font-size:smaller"> | ||
# Wakano, J. Y. & Hauert, Ch. (2011) J. theor. Biol. 268 30-38 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.09.036 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.09.036]. | |||
# Wakano, J. Y., Nowak, M. A. & Hauert, Ch. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106 7910-7914 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0812644106 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812644106]. | |||
# Hauert, Ch., Wakano, J. Y. & Doebeli, M. (2008) Theor. Pop. Biol. '''73''', 257-263 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tpb.2007.11.007 doi:10.1016/j.tpb.2007.11.007]. | |||
# Hauert, C., Holmes, M. & Doebeli, M. (2006) Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B '''273''', 2565-2570 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2006.3600 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.3600]. | |||
</div> | |||
|} | |||
{{-}} | |||
== [[Origin of Cooperators and Defectors]] == | |||
{| | |||
| style="vertical-align:top" |[[Image:Origin of cooperators and defectors.gif|left|160x160px|link=Origin of Cooperators and Defectors]] | |||
| style="vertical-align:top" |Tutorial on the gradual evolution of distinct cooperative and defective behavioral patterns through evolutionary branching into separate trait groups characterized by high and low cooperative investments. This is based on a model that extends the classical Snowdrift game to continuously varying degrees of cooperation. Apart from evolutionary branching, this model exhibits rich dynamics that can be easily explored using this interactive tutorial. | |||
<div class="footnote"> | <div class="footnote" style="font-size:smaller"> | ||
# Killingback, T., Doebeli, M. & Hauert, Ch. (2010) Biological Theory 5, 3-6 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1162/BIOT_a_00019 doi: 10.1162/BIOT_a_00019]. | |||
# Doebeli, M., Hauert, C. & Killingback, T. (2004) Science '''306''', 859-862 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1101456 doi: 10.1126/science.1101456]. | |||
</div> | |||
|} | |||
{{-}} | |||
Tutorial on | == [[2×2 Games]] == | ||
{| | |||
| style="width:160px; text-align:center; vertical-align:top" | [[Image:Cover IJBC 2002.12.png|center|160x160px|link=2×2 Games]] | |||
| style="vertical-align:top" | Tutorial on 2×2 games in populations with different structures. 2×2 games describe a rich set of pairwise interactions among individuals. The most prominent game is certainly the Prisoner's Dilemma which has become the paradigm to discuss the emergence of cooperative behavior. If players are arranged on regular lattices, many of these games produce fascinating spatio-temporal patterns. This tutorial provides a hands-on experience of this dynamical world. | |||
<div class="footnote"> Hauert, C. | <div class="footnote" style="font-size:smaller"> | ||
# Hauert, C. (2002) Int. J. of Bifurcation & Chaos '''12''' 1531-1548 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S0218127402005273 doi: 10.1142/S0218127402005273]. | |||
# Hauert, C. (2001) Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 268, 761-769 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2000.1424 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2000.1424]. | |||
</div> | |||
|} | |||
{{-}} | |||
<!-- | |||
== [[Introduction]] == | |||
[[Image:Founding fathers of Game Theory.gif|left|border|160x160px]] | |||
Quick introduction covering the basic ideas of evolutionary game theory illustrated with many examples. This section briefly introduces classic games such as the Prisoner's Dilemma, the Hawk-Dove- or Snowdrift game and the Rock-Scissors-Paper game. It is intended as an overview of the many features and capabilities of the interactive ''EvoLudo'' simulator. | |||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
<!-- | |||
== [[Via freedom to coercion: the emergence of costly punishment]] == | |||
[[Image:Via freedom to coercion.gif|left|160x160px]] | |||
Tutorial on the role of voluntary participation in joint effort games for the evolution of costly punishing behavior. The freedom to withdraw from common enterprises leads to the enforcement of social norms. Joint enterprises which are compulsory rather than voluntary are less likely to lead to cooperation. | |||
<div class="footnote"> | <div class="footnote"> Hauert, C., Traulsen, A., Brandt, H., Nowak, M. A. & Sigmund, K. (2007) ''Via freedom to coercion: the emergence of costly punishment,'' ''Science'' '''316''', 1905-1907. </div> | ||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
<!-- | |||
== [[Synergy & discounting of cooperation in social dilemmas]] == | |||
[[Image:Synergy & discounting in social dilemmas.gif|left|160x160px]] | |||
Tutorial on cooperation in social dilemmas. Social dilemmas are characterized by a conflict of interest between the individuals and the group. The most prominent examples of social dilemmas are the prisoner's dilemma, the snowdrift game and public goods game. Based on the concept of synergistic or discounted accumulation of cooperative benefits we present a unifying framework to model cooperation in social dilemmas. | |||
<div class="footnote"> Hauert, C., Michor, F., Nowak, M. & Doebeli, M. (2006) J. theor. Biol. '''239''', 195-202.<br /> Hauert, C. (2006) J. theor. Biol. '''240''', 627-636. </div> | |||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
<!-- | |||
== [[Evolutionary dynamics on graphs]] == | == [[Evolutionary dynamics on graphs]] == | ||
[[Image:Evolutionary dynamics on graphs.gif|left|160x160px]] | |||
Tutorial on the fixation probability of mutants in structured populations where individuals are arranged on a graph. For a large class of graphs, the fixation probability does not depend on the details of the population structure and is identical to a homogenous population. All these graphs display the same characteristic balance between evolutionary selection and random drift. Nevertheless, the structure of the graph can have significant effects on the fixation probability ranging from complete suppression of selection to guaranteed fixation of advantageous mutants. | Tutorial on the fixation probability of mutants in structured populations where individuals are arranged on a graph. For a large class of graphs, the fixation probability does not depend on the details of the population structure and is identical to a homogenous population. All these graphs display the same characteristic balance between evolutionary selection and random drift. Nevertheless, the structure of the graph can have significant effects on the fixation probability ranging from complete suppression of selection to guaranteed fixation of advantageous mutants. | ||
<div class="footnote"> Lieberman, E., Hauert, C. & Nowak, M. (2005) Nature '''433''', 312-316.<br /> Ohtsuki, H., Hauert, C., Lieberman, E. & Nowak, M. (2006) Nature '''441''', 502-505. </div> | <div class="footnote"> Lieberman, E., Hauert, C. & Nowak, M. (2005) Nature '''433''', 312-316.<br /> Ohtsuki, H., Hauert, C., Lieberman, E. & Nowak, M. (2006) Nature '''441''', 502-505. </div> | ||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
! | <!-- | ||
== [[Cooperation in structured populations]] == | == [[Cooperation in structured populations]] == | ||
[[Image:Cooperation in structured populations.gif|left|border|160x160px]] | |||
Tutorial on the fate of cooperative behavior in two closely related evolutionary games: the Prisoner's Dilemma and the Snowdrift (Hawk-Dove) game. The population structure then determines whether the evolution and maintenance of cooperation is promoted or hindered. In particular, this interactive tutorial illustrates that, in contrast to the Prisoner's Dilemma, spatial structure can be detrimental to cooperation in the Snowdrift game. | Tutorial on the fate of cooperative behavior in two closely related evolutionary games: the Prisoner's Dilemma and the Snowdrift (Hawk-Dove) game. The population structure then determines whether the evolution and maintenance of cooperation is promoted or hindered. In particular, this interactive tutorial illustrates that, in contrast to the Prisoner's Dilemma, spatial structure can be detrimental to cooperation in the Snowdrift game. | ||
<div class="footnote"> Hauert, C. & Doebeli, M. (2004) Nature '''428''', 643-646. </div> | <div class="footnote"> Hauert, C. & Doebeli, M. (2004) Nature '''428''', 643-646. </div> | ||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
! | <!-- | ||
== [[Voluntary Public Goods Games]] == | == [[Voluntary Public Goods Games]] == | ||
[[Image:Voluntary Public Goods Games.gif|left|border|160x160px]] | |||
Tutorial on voluntary participation in public goods games. Most of the literature on cooperation in social dilemmas assumes that interactions are compulsory. In most real-life situations, however, individuals may choose to opt out whenever a public enterprise appears too risky. This results in a rock-scissors-paper type dominance of cooperators, defectors and loners (those that do not participate). Volunteering can maintain cooperation in mixed populations and results in fascinating spatio-temporal patterns in spatial settings. | Tutorial on voluntary participation in public goods games. Most of the literature on cooperation in social dilemmas assumes that interactions are compulsory. In most real-life situations, however, individuals may choose to opt out whenever a public enterprise appears too risky. This results in a rock-scissors-paper type dominance of cooperators, defectors and loners (those that do not participate). Volunteering can maintain cooperation in mixed populations and results in fascinating spatio-temporal patterns in spatial settings. | ||
<div class="footnote"> Hauert, C., De Monte, S., Hofbauer, J. & Sigmund, K. (2002) Science '''296''' 1129-1132.<br /> Hauert, C., De Monte, S., Hofbauer, J. & Sigmund, K. (2002) J. theor. Biol. '''218''' 187-194. </div> | <div class="footnote"> Hauert, C., De Monte, S., Hofbauer, J. & Sigmund, K. (2002) Science '''296''' 1129-1132.<br /> Hauert, C., De Monte, S., Hofbauer, J. & Sigmund, K. (2002) J. theor. Biol. '''218''' 187-194. </div> | ||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
! | <!-- | ||
== [[Public goods games]] == | == [[Public goods games]] == | ||
[[Image:Public goods games.gif|left|border|160x160px]] | |||
Tutorial on public goods games in populations with different structures. Public goods games essentially represent a generalization of the pairwise prisoner's dilemma interactions to groups of arbitrary size. In spatially extended populations, where individuals interact within a limited local neighborhood, cooperators can persist through cluster formation. Variations of the value of the public good result in a critical phase transition which relates to percolation phenomena from condensed matter physics. | Tutorial on public goods games in populations with different structures. Public goods games essentially represent a generalization of the pairwise prisoner's dilemma interactions to groups of arbitrary size. In spatially extended populations, where individuals interact within a limited local neighborhood, cooperators can persist through cluster formation. Variations of the value of the public good result in a critical phase transition which relates to percolation phenomena from condensed matter physics. | ||
<div class="footnote"> Szabó, G. & Hauert, C. (2002) Phys. Rev. Lett. '''89''' (11) 118101. </div> | <div class="footnote"> Szabó, G. & Hauert, C. (2002) Phys. Rev. Lett. '''89''' (11) 118101. </div> | ||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
! | <!-- | ||
== [[Reward, punishment and reputation]] == | == [[Reward, punishment and reputation]] == | ||
[[Image:Reward, punishment & reputation.gif|left|border|160x160px]] | |||
Tutorial on effects of reward, punishment and reputation in Public Goods games. Various experimental studies on social dilemmas have shown that punishment is very efficient in creating incentives for cooperative behavior. Reward, however, is considerably less efficient. The underlying mechanisms are illustrated with a simple game theoretical model. | Tutorial on effects of reward, punishment and reputation in Public Goods games. Various experimental studies on social dilemmas have shown that punishment is very efficient in creating incentives for cooperative behavior. Reward, however, is considerably less efficient. The underlying mechanisms are illustrated with a simple game theoretical model. | ||
<div class="footnote"> Sigmund, K., Hauert, C. & Nowak, M. (2001) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA '''98''', 10757-10762.<br /> Brandt, H., Hauert, C. & Sigmund, K. (2003) Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B '''270''', 1099-1104. </div> | <div class="footnote"> Sigmund, K., Hauert, C. & Nowak, M. (2001) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA '''98''', 10757-10762.<br /> Brandt, H., Hauert, C. & Sigmund, K. (2003) Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B '''270''', 1099-1104. </div> | ||
{{-}} | |||
--> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:52, 31 August 2016
Evolutionary graph theory
 |
Tutorial on evolutionary graph theory, which provides a formal approach to describe the spreading and fixation (or extinction) of a mutant type in structured populations. Interestingly, the fixation probabilities remain unaffected by the underlying structure for a large class of graphs. However, some graphs may act either as amplifiers or suppressors of selection by increasing or decreasing the fixation probabilities as compared to unstructured populations. In contrast, fixation and absorption times are very sensitive to changes in the graph structure and hence vary greatly even for graphs that leave fixation probabilities unchanged. Even though fixation times are, in general, not preserved between graphs, symmetries of a graph can at least ensure that fixation times do not depend on the initial location of the mutant. This summarizes research efforts that span over a decade, including:
|
Stochastic dynamics in finite populations
 |
Tutorial on the stochastic dynamics arising through demographic noise and mutations in finite populations of size \(N\). Comparisons of the deterministic replicator dynamics in the limit of infinite population sizes \(N\to\infty\) to the stochastic dynamics generated by stochastic differential equations, which are derived from a microscopic description of elementary changes in the population, as well as to results from individual based simulations.
|
Evolutionary Games and Population Dynamics
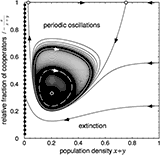 |
Tutorial on frequency dependent selection in populations of varying size. The classic replicator dynamics assumes constant (infinite) population sizes and thus neglects the ecology of the population. Linking ecological dynamics and evolutionary games generates fascinating and rich dynamical behavior. Most importantly, however, this reveals a new mechanism for maintaining cooperation through negative feedback between population densities and the size of interaction groups.
|
Origin of Cooperators and Defectors
 |
Tutorial on the gradual evolution of distinct cooperative and defective behavioral patterns through evolutionary branching into separate trait groups characterized by high and low cooperative investments. This is based on a model that extends the classical Snowdrift game to continuously varying degrees of cooperation. Apart from evolutionary branching, this model exhibits rich dynamics that can be easily explored using this interactive tutorial.
|
2×2 Games
 |
Tutorial on 2×2 games in populations with different structures. 2×2 games describe a rich set of pairwise interactions among individuals. The most prominent game is certainly the Prisoner's Dilemma which has become the paradigm to discuss the emergence of cooperative behavior. If players are arranged on regular lattices, many of these games produce fascinating spatio-temporal patterns. This tutorial provides a hands-on experience of this dynamical world.
|
