Evolutionary Kaleidoscopes in the Prisoner's Dilemma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== | ==EvoLudoLab== | ||
{{ | {{EvoLudoLab:2x2| | ||
options="--delay 200 --view 0 --reportfreq 1.0 --popsize 101x --popupdate s --playerupdate b | options="--game 2x2 --delay 200 --view 0 --reportfreq 1.0 --popsize 101x --popupdate s --playerupdate b --geometry n --intertype all --init 0,1 --inittype kaleidoscope --reward 1.0 --punishment 0.0 --temptation 1.4 --sucker 0.0"| | ||
title=Spatial Prisoner's Dilemma: evolutionary kaleidoscopes| | title=Spatial Prisoner's Dilemma: evolutionary kaleidoscopes| | ||
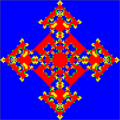
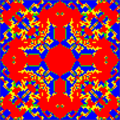
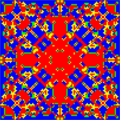
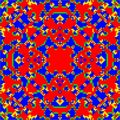
doc=For symmetrical initial configurations and determinsitic update rules fascinating spatio-temporal patterns resembling evolutionary kaleidoscopes can emerge in spatially structured populations where individuals are arranged on a lattice and interact only within a limited local neighborhood. Different values for the paramters <math>R, S, T</math> and <math>P</math> give rise to different types of kaleidoscopes. Here we set <math>R = 1, P = 0, S = 0.0</math> and<math>T = 1.4</math> and individuals interact with their four nearest neighbors on a square <math>101\times 101</math> lattice with periodic boundary conditions. | doc=For symmetrical initial configurations and determinsitic update rules fascinating spatio-temporal patterns resembling evolutionary kaleidoscopes can emerge in spatially structured populations where individuals are arranged on a lattice and interact only within a limited local neighborhood. Different values for the paramters <math>R, S, T</math> and <math>P</math> give rise to different types of kaleidoscopes. Here we set <math>R = 1, P = 0, S = 0.0</math> and<math>T = 1.4</math> and individuals interact with their four nearest neighbors on a square <math>101\times 101</math> lattice with periodic boundary conditions. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:48, 27 May 2024
For deterministic update rules (synchronous lattice update, best player in neighborhood reproduces) and symmetrical initial configurations this can lead to fascinating spatio-temporal patterns. Such evolutionary kaleidoscopes are certainly only of limited scientific interest but they do have quite some entertainment value.
EvoLudoLab
| Color code: | Cooperators | Defectors |
|---|---|---|
| New cooperator | New defector |
| Payoffs: | Low High
|
|---|
Note: The gradient of the payoff scale is augmented by pale shades of the strategy colours to mark payoffs that are achieved in homogeneous populations of the corresponding type.
Spatial Prisoner's Dilemma: evolutionary kaleidoscopes
For symmetrical initial configurations and determinsitic update rules fascinating spatio-temporal patterns resembling evolutionary kaleidoscopes can emerge in spatially structured populations where individuals are arranged on a lattice and interact only within a limited local neighborhood. Different values for the paramters and give rise to different types of kaleidoscopes. Here we set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R = 1, P = 0, S = 0.0} and and individuals interact with their four nearest neighbors on a square lattice with periodic boundary conditions.
Patient people will find that the evolving patterns come to a sudden an unexpected end after more than 200'000 generations (MC steps) when the system relaxes into a cyclic state with short period. The time until an absorbing or cyclic state with short period is reached sensitively depends on the lattice size. Interestingly there is no simple relation between system size and relaxation time.
Data views
| Snapshot of the spatial arrangement of strategies. | |
| Time evolution of the strategy frequencies. | |
| Snapshot of the spatial distribution of payoffs. | |
| Time evolution of average population payoff bounded by the minimum and maximum individual payoff. | |
| Snapshot of payoff distribution in population. | |
| Degree distribution in structured populations. | |
| Statistics of fixation probabilities. | |
| Statistics of fixation and absorption times. | |
| Statistics of the stationary distribution of the numbers of each strategic type. Note, only available for non-zero mutation rates. | |
| Message log from engine. |
Module parameters
The list below describes only the few parameters related to the Prisoner's Dilemma, Snowdrift and Hawk-Dove games. Follow the link for a complete list and detailed descriptions of the user interface and further parameters such as spatial arrangements or update rules on the player and population level.
- --paymatrix <a00,a01;a10,a11>
- 2x2 payoff matrix. Type \(A\) has index 0 and type \(B\) index 1.
- --inittype <type>
- type of initial configuration:
- frequency <f0>,<f1>...
- random distribution with given trait frequencies, f0, f1,.... Note, only available for frequency based modules and models.
- density <d0>,<d1>...
- initial trait densities <d1,...,dn>. Note, only available for density based modules and models.
- uniform
- uniform random distribution, equal frequencies of all traits.
- monomorphic <t>[,<v>]
- monomorphic initialization with trait t. Note, for modules with variable population densities, the optional parameter v indicates the initial frequency of vacant sites. If omitted the monomorphic trait is initialized at its (estimated) carrying capacity.
- mutant <m>,<r>[,<v>]
- single mutant with trait m in homogeneous resident population of type r. The mutant is placed in a location selected uniformly at random (mutants arising through cosmic rays). Note, for modules with variable population densities, the optional parameter v indicates the initial frequency of vacant sites. If omitted the resident trait is initialized at its (estimated) carrying capacity.
- temperature <m>,<r>[,<v>]
- single mutant with trait m in homogeneous resident population of type r. The mutant is placed in a location selected proportional to the in-degree of nodes (temperature initialization, mutants arising through errors in reproduction). Note, for modules with variable population densities, the optional parameter v indicates the initial frequency of vacant sites. If omitted the resident trait is initialized at its (estimated) carrying capacity.
- stripes
- stripes of traits. Note, only available for 2D lattices.
- kaleidoscopes
- configurations that produce evolutionary kaleidoscopes for deterministic updates (players and population). Note, only available for some modules.
Note, for modules that admit multiple species, the initialization types for each species can be specified as an array separated by ;. With more species than initialization types, they are assigned in a cyclical manner.