Parameters/Player: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Navbox | {{Navbox | ||
|title= | |title=''EvoLudo'' Documentation | ||
|navbar=off | |navbar=off | ||
|list1=[[ | |list1=[[Graphical User Interface|Graphical User Interface]] | ||
| | |list2=[[Parameters|Parameters]]{{·}} [[Data Views|Data Views]] | ||
|list3=[[Parameters/Game|Game]]{{·}} [[Parameters/Player|Player]]{{·}} [[Parameters/Population|Population]]{{·}} [[Parameters/Structure|Structure]]{{·}} [[Parameters/Misc|Miscellaneous]]{{·}} [[Parameters/PDE|PDE]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
Image:Params Player.png| | Image:Params Player.png| | ||
rect 80 26 136 47 [[Parameters | rect 80 26 136 47 [[Parameters/Game|Characteristics of interactions]] | ||
rect 137 26 196 47 [[Parameters/Player|Updating players]] | rect 137 26 196 47 [[Parameters/Player|Updating players]] | ||
rect 197 26 286 47 [[Parameters/Population|Updating the population]] | rect 197 26 286 47 [[Parameters/Population|Updating the population]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
rect 367 26 418 47 [[Parameters/Misc|Miscellaneous - mutations, migration, initialization]] | rect 367 26 418 47 [[Parameters/Misc|Miscellaneous - mutations, migration, initialization]] | ||
rect 419 26 465 47 [[Parameters/PDE|Numerical integration of PDE's]] | rect 419 26 465 47 [[Parameters/PDE|Numerical integration of PDE's]] | ||
rect 0 48 518 279 [[ | rect 0 48 518 279 [[Parameters/Player|Parameter settings for updating the players]] | ||
rect 0 280 129 310 [[# | rect 0 280 129 310 [[Parameters#Bottom Panel|Discard changes, close parameter panel]] | ||
rect 130 280 257 310 [[# | rect 130 280 257 310 [[Parameters#Bottom Panel|Discard changes, revert to previous settings]] | ||
rect 258 280 387 310 [[# | rect 258 280 387 310 [[Parameters#Bottom Panel|Apply changes]] | ||
rect 388 280 518 310 [[# | rect 388 280 518 310 [[Parameters#Bottom Panel|Apply changes, close parameter panel]] | ||
desc none | desc none | ||
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 34: | ||
:;best reference: | :;best reference: | ||
::the focal player adopts the best strategy among the players of the sampled reference/model group and keeps it's strategy if no one is performing better. This is a fully deterministic update rule. In special situations, i.e. in the case of ties, two additional rules are required to preserve the | ::the focal player adopts the best strategy among the players of the sampled reference/model group and keeps it's strategy if no one is performing better. This is a fully deterministic update rule. In special situations, i.e. in the case of ties, two additional rules are required to preserve the deterministic updating. (i) if a reference player has the same score as the focal player then the focal player keeps it's strategy. (ii) if there are more than two strategies and two reference players with different strategies have a higher score than the focal player then the focal player adopts a strategy in a cyclic fashion depending on its current strategy. For example in the voluntary public goods game there are the three strategic types cooperate, defect and loner. A cooperating focal player with defecting and loner reference players that perform equally well but better than the cooperator, switches to the defector strategy. Similarly, a defector switches to loner and a loner to cooperator. This reflects the underlying cyclic dominance of the three strategies. It is important to note that these additional rules can always be avoided by choosing non-degenerate payoff parameters, i.e. parameters where the payoffs of different strategic types always differ. | ||
:;best-reply: | :;best-reply: | ||
| Line 53: | Line 55: | ||
;Player update prob: | ;Player update prob: | ||
:probability that a player | :probability that a player reassess and updates its strategic behavior. | ||
;Player update noise: | ;Player update noise: | ||
Latest revision as of 09:33, 15 March 2010
| |||||||||||
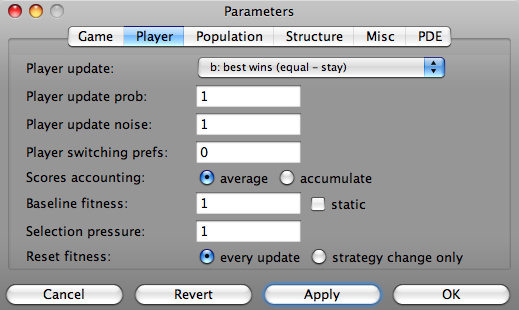
Panel to set the parameters for updating players
- Player update
- determines the imitation/replication behavior of the players and how their strategies change over time.
- best reference
- the focal player adopts the best strategy among the players of the sampled reference/model group and keeps it's strategy if no one is performing better. This is a fully deterministic update rule. In special situations, i.e. in the case of ties, two additional rules are required to preserve the deterministic updating. (i) if a reference player has the same score as the focal player then the focal player keeps it's strategy. (ii) if there are more than two strategies and two reference players with different strategies have a higher score than the focal player then the focal player adopts a strategy in a cyclic fashion depending on its current strategy. For example in the voluntary public goods game there are the three strategic types cooperate, defect and loner. A cooperating focal player with defecting and loner reference players that perform equally well but better than the cooperator, switches to the defector strategy. Similarly, a defector switches to loner and a loner to cooperator. This reflects the underlying cyclic dominance of the three strategies. It is important to note that these additional rules can always be avoided by choosing non-degenerate payoff parameters, i.e. parameters where the payoffs of different strategic types always differ.
- best-reply
- based on the sampled reference/model group of players, the focal player chooses the best performing strategy. This can be any strategy available and is not restricted to the strategy set of the sample group (c.f. best reference updating above). For this reason this is called an innovative update rule. Traditionally, the focal player has complete information on the population composition, i.e. on the abundance of the different strategies in terms of frequencies or numbers. This assumes well-mixed populations, i.e. mean-field scenarios with random pairings of players. In structured populations, however, the pool for sampling reference players is restricted to the local neighborhood.
- imitate/replicate (better only)
- x
- imitate/replicate (linear)
- x
- imitate proportional to absolute payoff
- x
- 'thermal' update
- x
- Moran process (birth-death or death-birth)
- For population updating based on the Moran process, all the player updating parameters are ignored.
- Player update prob
- probability that a player reassess and updates its strategic behavior.
- Player update noise
- This parameter affects only the thermal player update. The player may not have complete information on the exact payoff of the sampled reference/model group of players which leads to uncertainties in the decisions.
- Player switching prefs
- This parameter affects only the imitate proportional to payoff difference player update. Players may have smaller or larger preferences for switching their strategies. The preference ranges continuously from -1 to +1 where for -1 players never switch and for +1 they switch with certainty whenever at least one better performing player is found in the sampled reference/model group of players.
- Scores accounting
- x.
- Baseline fitness
- x.
- Selection pressure
- x.
- Reset fitness
- x.
